Java Swings
Difference between applets and swings,
Swings
|
Applets
|
Swing is light weight Component.
Java swing components are platform-independent. |
Applet is heavy weight Components
AWT components are platform-dependent. |
Swing Using UIManager. Swing have look and feel according to
user view u can change look and feel.
|
Applet Does not provide this
facility
|
Swing uses for stand lone Applications ,Swing have main method to execute the
program.
|
Applet need HTML code for Run the
Applet
|
Swing uses MVC Model view Controller.
|
Applet not
|
Swing have its own Layout ..like most
popular Box Layout
|
Applet uses AWT Layouts..like flow
layout
|
Swing have some Thread rules.
|
Applet doesn't have any rule.
|
To
execute Swing no need any
browser By which we can create stand alone application But Here we have to
add container and maintain all action control with in frame container.
|
To
execute Applet programe we
should need any one browser like Appletviewer,web browser. Because Applet using browser container to run
and all action control with in browser container.
|
Java Swing tutorial is a part of Java Foundation Classes (JFC) that is used to create window-based applications. It is built on the top of AWT (Abstract Windowing Toolkit) API and entirely written in java.
Unlike AWT, Java Swing provides platform-independent and lightweight components.
The javax.swing package provides classes for java swing API such as JButton, JTextField, JTextArea, JRadioButton, JCheckbox, JMenu, JColorChooser etc.
JFC
The Java Foundation Classes (JFC) are a set of GUI components which simplify the development of desktop applications.
The hierarchy of java swing API is given below.
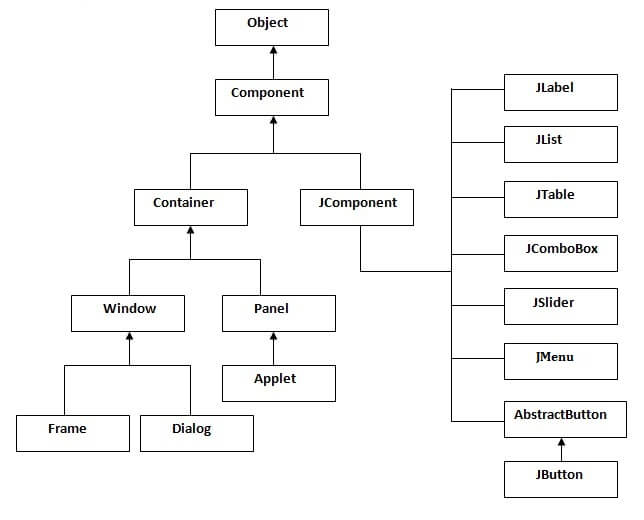
The
methods of Component class are widely used in java swing that are given below,
Method
|
Description
|
public
void add(Component c)
|
add a
component on another component.
|
public
void setSize(int width,int height)
|
sets
size of the component.
|
public
void setLayout(LayoutManager m)
|
sets
the layout manager for the component.
|
public
void setVisible(boolean b)
|
sets
the visibility of the component. It is by default false.
|
There are two ways to create a frame,
- By creating the object of Frame class (association)
- By extending Frame class (inheritance)
We can write the code of swing inside the main(), constructor or any other method.
Example,
import javax.swing.*;
public class SwingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame f=new JFrame();//creating instance of JFrame
JButton b=new JButton("click");//creating instance of JButton
b.setBounds(130,100,100, 40);//x axis, y axis, width, height
f.add(b);//adding button in JFrame
f.setSize(400,500);//400 width and 500 height
f.setLayout(null);//using no layout managers
f.setVisible(true);//making the frame visible
}
}
We can also write all the codes of creating JFrame, JButton and method call inside the java constructor,
import javax.swing.*;
public class Simple {
JFrame f;
Simple(){
f=new JFrame();//creating instance of JFrame
JButton b=new JButton("click");//creating instance of JButton
b.setBounds(130,100,100, 40);
f.add(b);//adding button in JFrame
f.setSize(400,500);//400 width and 500 height
f.setLayout(null);//using no layout managers
f.setVisible(true);//making the frame visible
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Simple();
}
}
We can also inherit the JFrame class, so there is no need to create the instance of JFrame class explicitly.
import javax.swing.*;
public class Simple2 extends JFrame{//inheriting JFrame
JFrame f;
Simple2(){
JButton b=new JButton("click");//create button
b.setBounds(130,100,100, 40);
add(b);//adding button on frame
setSize(400,500);
setLayout(null);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Simple2();
}
}
No comments:
Post a Comment