Overview
- A stream can be defined as a sequence of data.
- Input Stream is used to read data from a source and the Output Stream is used for writing data to a destination.
- Java provides strong but flexible support for I/O related to Files and networks.
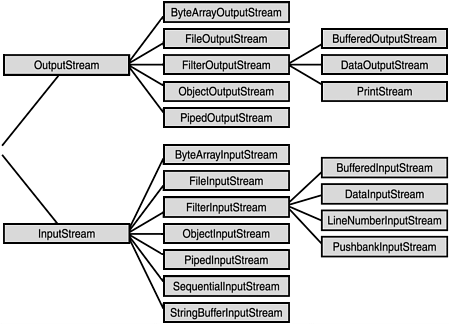
Byte stream is defined by using two abstract class at the top of hierarchy, they are Input Stream and Output Stream.
Java byte streams are used to perform input and output of 8-bit bytes. Though there are many classes related to byte streams but the most frequently used classes are ,FileInputStream and FileOutputStream
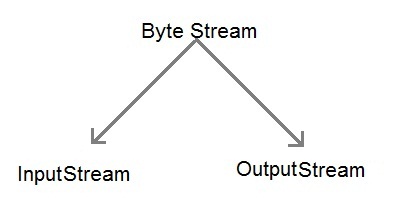
These two abstract classes have several concrete classes that handle various devices such as disk files, network connection etc.
Some important Byte stream classes.
| Stream class | Description |
|---|---|
| BufferedInputStream | Used for Buffered Input Stream. |
| BufferedOutputStream | Used for Buffered Output Stream. |
| DataInputStream | Contains method for reading java standard datatype |
| DataOutputStream | An output stream that contain method for writing java standard data type |
| FileInputStream | Input stream that reads from a file |
| FileOutputStream | Output stream that write to a file. |
| InputStream | Abstract class that describe stream input. |
| OutputStream | Abstract class that describe stream output. |
| PrintStream | Output Stream that contain print() and println() method |
These classes define several key methods. Two most important are
read(): reads byte of data.write(): Writes byte of data.
Example,
import java.io.*; public class CopyFile { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { FileInputStream in = null; FileOutputStream out = null; try { in = new FileInputStream("input.txt"); out = new FileOutputStream("output.txt"); int c; while ((c = in.read()) != -1) { out.write(c); } }finally { if (in != null) { in.close(); } if (out != null) { out.close(); } } } }
Character Stream Classes
Character stream is also defined by using two abstract class at the top of hierarchy, they are Reader and Writer.
Java Byte streams are used to perform input and output of 8-bit bytes, where as JavaCharacter streams are used to perform input and output for 16-bit unicode.
Though there are many classes related to character streams but the most frequently used classes are ,FileReader and FileWriter.
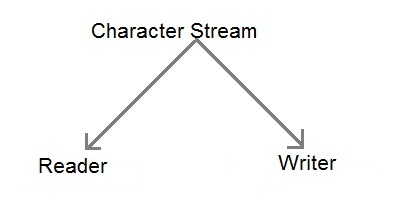
These two abstract classes have several concrete classes that handle unicode character.
Some important Character stream classes.
| Stream class | Description |
|---|---|
| BufferedReader | Handles buffered input stream. |
| BufferedWriter | Handles buffered output stream. |
| FileReader | Input stream that reads from file. |
| FileWriter | Output stream that writes to file. |
| InputStreamReader | Input stream that translate byte to character |
| OutputStreamReader | Output stream that translate character to byte. |
| PrintWriter | Output Stream that contain print() and println() method. |
| Reader | Abstract class that define character stream input |
| Writer | Abstract class that define character stream output |
Reading Console Input
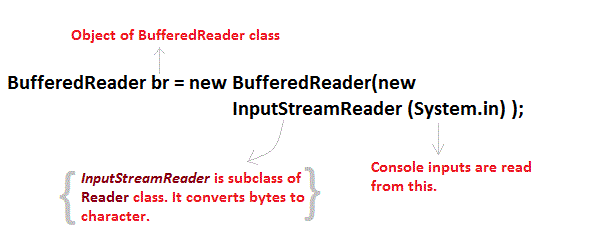
We use the object of BufferedReader class to take inputs from the keyboard.
Reading Characters
read() method is used with BufferedReader object to read characters. As this function returns integer type value has we need to use typecasting to convert it into char type.int read() throws IOException
Below is a simple example explaining character input.
class CharRead
{
public static void main( String args[])
{
BufferedReader br = new Bufferedreader(new InputstreamReader(System.in));
char c = (char)br.read(); //Reading character
}
}
Reading Strings
To read string we have to use
readLine() function with BufferedReader class's object.String readLine() throws IOException
Program to take String input from Keyboard in Java
import java.io.*;
class MyInput
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String text;
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
text = br.readLine(); //Reading String
System.out.println(text);
}
}
Program to read from a file using BufferedReader class
import java. Io *;
class ReadTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
File fl = new File("d:/myfile.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fl)) ;
String str;
while ((str=br.readLine())!=null)
{
System.out.println(str);
}
br.close();
fl.close();
}
catch (IOException e)
{ e.printStackTrace(); }
}
}
Program to write to a File using FileWriter class
import java. Io *;
class WriteTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
File fl = new File("d:/myfile.txt");
String str="Write this string to my file";
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(fl) ;
fw.write(str);
fw.close();
fl.close();
}
catch (IOException e)
{ e.printStackTrace(); }
}
}
Example
import java.io.*; public class CopyFile { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { FileReader in = null; FileWriter out = null; try { in = new FileReader("input.txt"); out = new FileWriter("output.txt"); int c; while ((c = in.read()) != -1) { out.write(c); } }finally { if (in != null) { in.close(); } if (out != null) { out.close(); } } } }
Byte vs characters streams,

No comments:
Post a Comment