Hash map class

HashMap<Integer,String> colorMap =new HashMap<Integer,String>();
colorMap .put(1,"Red");
colorMap .put(1,"Green");
colorMap .put(1,"Blue");
for(Map.Entry m:hm.entrySet()){
System.out.println(m.getKey()+" "+m.getValue());
}
Output:
1 Red
2 Green
3 Blue
Note :
HashSet contains only values whereas HashMap contains entry(key and value).
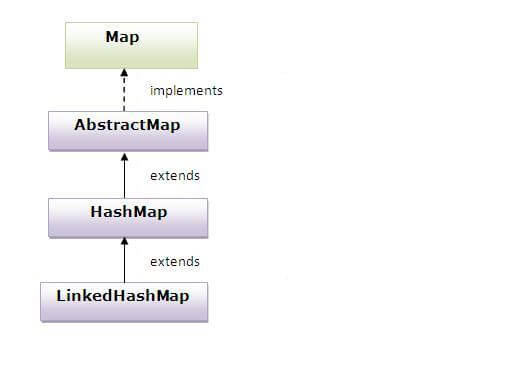
Linked Hash Map,
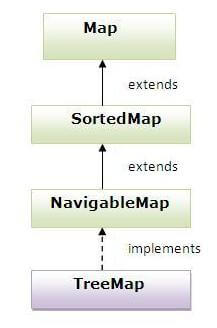
Tree Map
- A Hash Map contains values based on the key. It implements the Map interface and extends Abstract Map class.
- It contains only unique elements.
- It may have one null key and multiple null values.
- It maintains no order.
HashMap<Integer,String> colorMap =new HashMap<Integer,String>();
colorMap .put(1,"Red");
colorMap .put(1,"Green");
colorMap .put(1,"Blue");
for(Map.Entry m:hm.entrySet()){
System.out.println(m.getKey()+" "+m.getValue());
}
Output:
1 Red
2 Green
3 Blue
Note :
HashSet contains only values whereas HashMap contains entry(key and value).
Linked Hash Map,
- A LinkedHashMap contains values based on the key. It implements the Map interface and extends HashMap class.
- It contains only unique elements.
- It may have one null key and multiple null values.
- It is same as HashMap instead maintains insertion order.

Example,
LinkedHashMap<Integer,String> colorMap =new LinkedHashMap<Integer,String>();
- A Tree Map contains values based on the key. It implements the NavigableMap interface and extends Abstract Map class.
- It contains only unique elements.
- It cannot have null key but can have multiple null values.
- It is same as Hash Map instead maintains ascending order.

Example,
TreeMap<Integer,String> colorMap =new TreeMap<Integer,String>();
No comments:
Post a Comment