Vector,
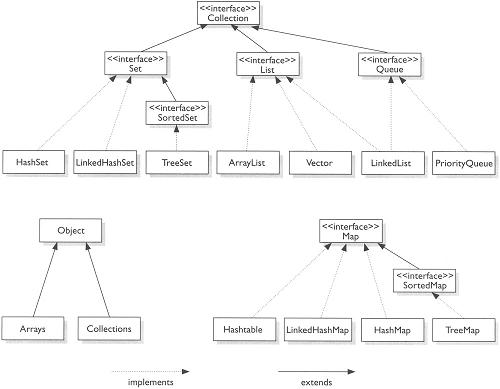
Vector implements a dynamic array. It is similar to ArrayList, but with two differences:

Vector implements a dynamic array. It is similar to ArrayList, but with two differences:
- Vector is synchronized.
- Vector contains many legacy methods that are not part of the collections framework.
- The Vector class implements a growable array of objects.
Like an array, it
contains components that can be accessed using an
integer index. However, the size of a Vector can grow or shrink as
needed to accommodate adding and removing items after the Vector has
been created.
- See more at: http://www.java2novice.com/java-collections-and-util/vector/#sthash.Ni1lt0cw.dpuf
Vector proves to be very useful if you don't know the size of the
array in advance or you just need one that can change sizes over the
lifetime of a program.
The Vector class supports four constructors. The first form creates a default vector, which has an initial size of 10:
Vector methods and its defintions,
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/Vector.html
Here are the Vector constructors:
The first form creates a default vector, which has an initial size of 10.
The second form creates a vector whose initial capacity is specified by size.
The third form creates a vector whose initial capacity is specified by size and whose increment is specified by incr.
The increment specifies the number of elements to allocate each time that a vector is resized upward. The fourth form creates a vector that contains the elements of collection c. This constructor was added by Java 2.
The Vector class supports four constructors. The first form creates a default vector, which has an initial size of 10:
Vector methods and its defintions,
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/Vector.html
Here are the Vector constructors:
Vector( )
Vector(int size)
Vector(int size, int incr)
Vector(Collection c)
The first form creates a default vector, which has an initial size of 10.
The second form creates a vector whose initial capacity is specified by size.
The third form creates a vector whose initial capacity is specified by size and whose increment is specified by incr.
The increment specifies the number of elements to allocate each time that a vector is resized upward. The fourth form creates a vector that contains the elements of collection c. This constructor was added by Java 2.
Example,
Get the vector capacity,
v.capacity();
// initial size is 3, increment is 2
Vector v = new Vector(3, 2);
v.addElement(new Integer(1)); Get the vector capacity,
v.capacity();
No comments:
Post a Comment